Weitere Unterabschnitte: Geschichte der DV | Geschichte der DV 2 | Rechenmaschinen | Rechenmaschinen 2 | Programmsteuerung 1 | Programmsteuerung 2 | Programmsteuerung 3 | 1. Computergeneration | 2. Computergeneration | 3. Computergeneration | 4. Computergeneration | 5.-6. Computergeneration | Geschichte der IT | Geschichte des Autos 1 | Geschichte des Autos 2 | Geschichte des Autos 3
1. Computergeneration
Eckert, John W. Mauchly (1946 ENIAC)
ENIAC_Tubes.jpg
Elektronenröhre (1946)
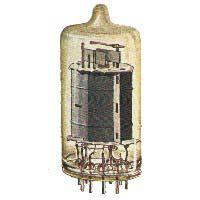
Elektronenröhre (1946)
Bild: Mit freundlicher Genehmigung Dr. Gerhard Staude 2009
Die unberechtigte Nutzung ist nicht gestattet.
Die unberechtigte Nutzung ist nicht gestattet.
Sollte evtl. verwendetes material gegen Copyright-Rechte verstoßen, werde ich dieses Material umgehend aus der Seite entfernen.
IBM vacuum tubes
IBM Card Sorter

IBM was a pioneer when it came to punch cards, an early way of storing data and programs. One of the ways in which they helped to gain that reputation was by building automated card sorters and collators, which could work exceptionally fast, up to two thousand cards per minute!
Bild: Pargon
Whirlwind
Cold War Computing – The SAGE System
Whirlwind 1 Computer

Bild: Alex Handy
Computer History Museum: Whirlwind

Bild: Marcin Wichary
Eckert, John W. Mauchly (1949 EDVAC)
EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Calculator) in den USA (Eckert, Mauchly, von Neumann)
Der EDVAC
EDVAC
Wilkes (1949 EDSAC)
University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory May 1949 members

University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory May 1949 members.
Top row, from left: D. Willis, J. Stanley, L. Foreman, G. Stevens, S. Barton, P. Farmer, P. Chamberlain
Middle row, from left: H. Smith, C. Mumford, H. Pye, A. Thomas, E. McKee, J. Steel
Bottom row, from left: R. Bonham-Carter, E. Mutch, W. Renwick, M. Wilkes, J. Bennett, D. Wheeler, B. Worsley
Copyright Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge. Reproduced by permission.
Maurice V. Wilkes – Wikipedia
Computer Science Diploma

Valedictory event for the Diploma, Cambridge Computer Lab, July 16 2008: Maurice Wilkes, watched by Andy Hopper
Bild: BillT
EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator) in England (Wilkes, von Neumann)